 -->
-->
3com mini pci 56k modem driver download for windows 10. Overview of the IEEE 1394 bus technology.
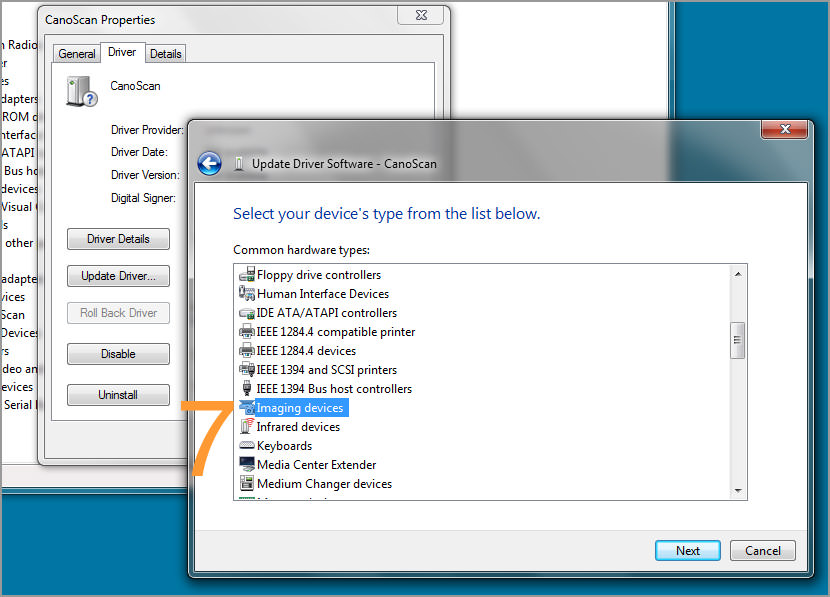
1394 OHCI Compliant Host Controller (Legacy) - Driver Download. Vendor: 1394 OHCI Compliant Host Controller. Windows 7 32-Bit Driver. Total Driver Versions: 1. The IEEE 1394 Driver Stack. Installing IEEE 1394 Device Drivers. Asynchronous I/O for IEEE 1394 Devices. Isochronous I/O for IEEE 1394 Devices. Modifying the 1394 Configuration ROM. IEEE 1394 Hardware Emulation Drivers. 1394 Samples and Diagnostic Tools. IEC-61883 Client Drivers.
To develop IEEE 1394 bus, you need these headers:
For the programming guide, see IEEE 1394 bus.
IOCTLs
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| IOCTL_1394_CLASS | An IEEE 1394 driver uses the IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL IRP, with IoControlCode IOCTL_1394_CLASS, to communicate with the bus driver. The driver has access to all operations provided by the IEEE 1394 bus and its host controller through this request. |
| IOCTL_61883_CLASS | An IEC-61883 client driver uses the IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL IRP with IoControlCode IOCTL_61883_CLASS to communicate with 1394 driver stack using the IEC-61883 protocol. |
Enumerations
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| CMP_CONNECT_TYPE | This enumeration specifies a connection type. |
| CMP_PLUG_LOCATION | This enumeration specifies the location of a plug. |
| CMP_PLUG_TYPE | This enumeration specifies the type of a plug. |
Functions
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| PBUS_RESET_ROUTINE | This is a caller-supplied function to be called by the protocol driver when the 1394 bus is reset. |
| PCMP_MONITOR_ROUTINE | This routine is called for plug monitoring. |
| PCMP_NOTIFY_ROUTINE | This routine is called for plug notification. |
Microsoft 1394 Driver Download For Windows 8.1
Structures
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| ADDRESS_FIFO | The ADDRESS_FIFO structure is an entry in a singly-linked list of MDLs used by the REQUEST_ALLOCATE_ADDRESS_RANGE IEEE 1394 bus request. |
| ADDRESS_OFFSET | The ADDRESS_OFFSET structure specifies the 48-bit address within a device's IEEE 1394 address space. |
| ADDRESS_RANGE | The ADDRESS_RANGE structure describes a range in a IEEE 1394 device's address space. |
| AV_61883_REQUEST | The AV_61883_REQUEST structure is used to pass requests to the IEC-61883 protocol driver. |
| AV_PCR | The AV_PCR structure specifies settings for an input or output plug. |
| BUS_GENERATION_NODE | The BUS_GENERATION_NODE structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_GetUnitInfo request to retrieve bus characteristics. |
| BUS_RESET_DATA | The BUS_RESET_DATA structure specifies the context for the extended bus reset notification routine. |
| BUS_RESET_NOTIFY | This structure is used to register or deregister the PBUS_RESET_ROUTINE callback. |
| CIP_ATTACH_FRAME | This structure is used in an attach frame request. |
| CIP_CANCEL_FRAME | The request cancels an attached frame buffer. A frame can be canceled while the stream is running. |
| CIP_DATA_FORMAT_VER2 | This structure is a CIP data format which is used by CMP_CONNECT_VER2. |
| CIP_DATA_FORMAT_VER3 | This structure is used by CipDataFormat. |
| CIP_FRAME | The CIP_FRAME structure describes a frame to be attached to an input or output plug. |
| CIP_LISTEN | This structure is used for a listen request. The request begins isochronous reception on the specified connection. |
| CIP_NOTIFY_INFO | The CIP_NOTIFY_INFO structure contains information about the frame. |
| CIP_STOP | This structure is used to stop transmission or reception. |
| CIP_TALK | This structure is used to begin transmission. |
| CIP_VALIDATE_INFO | The CIP_VALIDATE_INFO structure contains information about the frame. |
| CMP_CONNECT_VER2 | This structure contains information for a connection request. The request attempts to make a connection to a plug control register on the local host. |
| CMP_CONNECT_VER3 | This structure contains information for a connection request. |
| CMP_CREATE_PLUG | This structure is used to create a plug. |
| CMP_DELETE_PLUG | This structure is used to delete a plug.Av61883_CreatePlug. |
| CMP_DISCONNECT | This structure is used to break a connection. |
| CMP_GET_PLUG_HANDLE | This structure is used in getting the handle of a plug. |
| CMP_GET_PLUG_STATE | This structure is used in getting the state of a plug. |
| CMP_MONITOR_INFO | The CMP_MONITOR_INFO structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_MonitorPlugs request to allow a driver to monitor access to local oPCR and iPCR plugs. |
| CMP_MONITOR_PLUGS | This structure is used to monitor plug access. The request allows a driver to monitor all access to local oPCR and iPCR plugs. |
| CMP_NOTIFY_INFO | This structure is used by the PCMP_NOTIFY_ROUTINE callback. |
| CMP_SET_PLUG | This structure is used to assign settings to a plug. |
| CONFIG_ROM | The CONFIG_ROM structure is used to contain the first 24 bytes of an IEEE 1394 device's configuration ROM. |
| CYCLE_TIME | The CYCLE_TIME structure contains the IEEE 1394 isochronous cycle time. |
| FCP_FRAME | The FCP_FRAME structure describes a function control protocol (FCP) request. |
| FCP_GET_REQUEST | This structure is used for a get request. |
| FCP_REQUEST | This structure is used for a send request. |
| FCP_RESPONSE | The structure is used in a request yjsy retrieves the next FCP response from the queue of requests maintained by the IEC-61883 protocol driver. |
| FCP_SEND_RESPONSE | This structure is used for a send response. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO1 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO1 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel GET_HOST_UNIQUE_ID. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO2 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO2 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel GET_HOST_CAPABILITIES. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO3 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO3 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel = GET_POWER_SUPPLIED. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO4 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO4 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel = GET_PHYS_ADDR_ROUTINE. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO5 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO5 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel = GET_HOST_CONFIG_ROM. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO6 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO6 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request using u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel = GET_HOST_CSR_CONTENTS. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO7_W2K | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO7 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request with u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel set to GET_HOST_DMA_CAPABILITIES. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO7_WXP | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO7 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request with u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel set to GET_HOST_DMA_CAPABILITIES. |
| GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO8 | The GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO8 structure contains the data returned by a REQUEST_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFO request with u.GetLocalHostInformation.nLevel set to GET_HOST_DDI_VERSION. |
| GET_UNIT_CAPABILITIES | The GET_UNIT_CAPABILITIES structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_GetUnitInfo request to retrieve unit information about a device's capabilities. |
| GET_UNIT_IDS | The GET_UNIT_CAPABILITIES structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_GetUnitInfo request to retrieve device identifiers. |
| GET_UNIT_INFO | This structure is used to get unit information. |
| IO_ADDRESS | The IO_ADDRESS structure specifies the 1394 64-bit destination address for read, write and lock operations. |
| IPCR | The IPCR structure contains initialization values for an input plug. |
| IRB | Drivers use this structure to pass most requests to IEEE 1394 bus driver. |
| IRB_REQ_ALLOCATE_ADDRESS_RANGE | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 stack to carry out a request to allocate an address range. |
| IRB_REQ_ASYNC_LOCK | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 stack to carry out an asychronous lock request. |
| IRB_REQ_ASYNC_READ | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 stack to carry out an asynchronous read request. |
| IRB_REQ_ASYNC_STREAM | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out an asynchronous write request. |
| IRB_REQ_ASYNC_WRITE | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 stack to carry out an asynchronous write request. |
| IRB_REQ_BUS_RESET | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to create a bus reset request. |
| IRB_REQ_BUS_RESET_NOTIFICATION | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a bus reset notification request. |
| IRB_REQ_CONTROL | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a control request. |
| IRB_REQ_FREE_ADDRESS_RANGE | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 stack to carry out a free address range reqeust. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_1394_ADDRESS_FROM_DEVICE_OBJECT | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a Get1394AddressFromDeviceObject request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_CONFIG_ROM | This structure contains the fields necessary for the bus driver to carry out a GetConfigRom request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_CONFIGURATION_INFORMATION | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a GetConfigurationInformation request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_GENERATION_COUNT | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a GetGenerationCount request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_LOCAL_HOST_INFORMATION | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a GetLocalHostInformation request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_MAX_SPEED_BETWEEN_DEVICES | This structure contains the fields necessary in order for the Bus driver to carry out a GetMaxSpeedBetweenDevices request. |
| IRB_REQ_GET_SPEED_TOPOLOGY_MAPS | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a GetSpeedTopologyMaps request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_ALLOCATE_BANDWIDTH | This structure contains the fields necessary in order for the Bus driver to carry out an IsochAllocateBandwidth request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_ALLOCATE_CHANNEL | This structure contains the fields necessary in order for the 1394 bus driver to carry out an IsochAllocateChannel request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_ALLOCATE_RESOURCES_W2K | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a IsochAllocateResources request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_ALLOCATE_RESOURCES_WXP | This structure contains the fields necessary for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a IsochAllocateResources request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_ATTACH_BUFFERS | This structure contains the fields required for the 1394 bus driver to carry out a IsochAttachBuffers request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_DETACH_BUFFERS | This structure contains the fields required to carry out a IsochDetachBuffers request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_FREE_BANDWIDTH | This structure contains the fields necessary in order for the Bus driver to carry out an IsochFreeBandwidth request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_FREE_CHANNEL | This structure contains the fields required to carry out a IsochFreeChannel request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_FREE_RESOURCES | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a IsochFreeResources request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_LISTEN | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a ReqIsochListen request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_MODIFY_STREAM_PROPERTIES | This structure contains the fields necessary for the Bus driver to carry out an IsochModifyStreamProperties request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_QUERY_CURRENT_CYCLE_TIME | This structure contains the fields necessary for the Bus driver to carry out an IsochQueryCurrentCycleTime request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_QUERY_RESOURCES | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a IsochQueryResources request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_SET_CHANNEL_BANDWIDTH | This structure contains the fields necessary for the Bus driver to carry out an IsochSetChannelBandwidth request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_STOP | This structure contains the field necessary to carry out a IsochStop request. |
| IRB_REQ_ISOCH_TALK | This structure contains the field necessary to carry out a IsochTalk request. |
| IRB_REQ_RECEIVE_PHY_PACKETS | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a ReceivePhyPackets request. |
| IRB_REQ_SEND_PHY_CONFIGURATION_PACKET | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a SendPhyConfigurationPacket request. |
| IRB_REQ_SEND_PHY_PACKET | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a SendPhyPacket request. |
| IRB_REQ_SET_DEVICE_XMIT_PROPERTIES | This structure contains the fields necessary to carry out a SetDeviceXmitProperties request. |
| IRB_REQ_SET_LOCAL_HOST_PROPERTIES | This structure contains the fields required to carry out a SetLocalHostProperties request. |
| ISOCH_DESCRIPTOR | The ISOCH_DESCRIPTOR structure describes a buffer to be attached or detailed from a resource handle, using the REQUEST_ISOCH_ATTACH_BUFFERS and REQUEST_ISOCH_DETACH_BUFFERS requests. |
| NODE_ADDRESS | The NODE_ADDRESS structure specifies the 10-bit bus number and 6-bit node number that serve as the node address for a 1394 node. |
| NOTIFICATION_INFO_W2K | The bus driver passes NOTIFICATION_INFO to pass information to the driver-provided notification routine for a driver-allocated address range in the computer's IEEE 1394 address space. |
| NOTIFICATION_INFO_WXP | The bus driver passes NOTIFICATION_INFO to pass information to the driver-provided notification routine for a driver-allocated address range in the computer's IEEE 1394 address space. |
| OPCR | The OPCR structure contains initialization values for an output plug. |
| PHY_CONFIGURATION_PACKET | The PHY_CONFIGURATION_PACKET structure contains a raw PHY configuration packet. |
| SELF_ID | The SELF_ID structure contains a raw packet zero self-ID packet. See the IEEE 1394 Trade Association specification website for details. |
| SELF_ID_MORE | The SELF_ID_MORE structure contains a raw packet one, two, or three self-ID packet. See the IEEE 1394 specification for details. |
| SET_CMP_ADDRESS_TYPE | The SET_CMP_ADDRESS_TYPE structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_SetUnitInfo request to set the parameters that the IEC-61883 protocol driver should use when capturing and transmitting isochronous packets. |
| SET_FCP_NOTIFY | This structure is used for FCP notification. |
| SET_LOCAL_HOST_PROPS2 | SET_LOCAL_HOST_PROPS2 sets a lower bound on the value the bus will use for its gap count. |
| SET_LOCAL_HOST_PROPS3 | SET_LOCAL_HOST_PROPS3 contains the data necessary for defining or identifying one or more unit directories in the Configuration ROM of a 1394 Host Controller. |
| SET_UNIT_DIRECTORY | This structure is used to assign settings for a unit directory. |
| SET_UNIT_INFO | This structure is used to set unit information. |
| SPEED_MAP | The SPEED_MAP structure is stores a IEEE 1394 bus speed map. |
| TEXTUAL_LEAF | The TEXTUAL_LEAF structure describes the device description that can be stored in the Configuration ROM of devices that satisfy the PC 98 or PC 99 specifications. |
| TOPOLOGY_MAP | The TOPOLOGY_MAP structure is used to store an IEEE 1394 bus topology map. The relations between devices are found in the port members of the entries in TOP_Self_ID_Array. |
| UNIT_DDI_VERSION | The UNIT_DDI_VERSION structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_GetUnitInfo request to retrieve the current 61883 DDI version. |
| UNIT_DIAG_LEVEL | The UNIT_DDI_VERSION structure is used in conjunction with the Av61883_GetUnitInfo request to retrieve the current diag level |
| UNIT_ISOCH_PARAMS | The UNIT_ISOCH_PARAMS structure is used to get or set the parameters that the IEC-61883 protocol driver uses when capturing or transmitting isochronous packets. |
Windows 7 includes 1394ohci.sys, a new IEEE 1394 bus driver that supports faster speeds and alternative media as defined in the IEEE-1394b specification. The 1394ohci.sys bus driver is a single (monolithic) device driver, implemented by using the kernel-mode driver framework (KMDF). The legacy 1394 bus driver (available in earlier versions of Windows) includes multiple device drivers that were implemented by using the Windows Driver Model (WDM) in a port/miniport configuration. The 1394ohci.sys bus driver replaces the legacy port driver, 1394bus.sys, and the primary miniport driver, ochi1394.sys.
The new 1394ohci.sys bus driver is fully backward compatible with the legacy bus driver. This topic describes some of the known differences in behavior between the new and the legacy 1394 bus driver.
Note
The 1394ohci.sys driver is a system driver that is included in Windows. It is automatically loaded when you install a 1394 controller. This is not a redistributable driver that you can download separately.
I/O Request Completion

All I/O requests that are sent to the new 1394 bus driver return STATUS_PENDING because the 1394ohci.sys bus driver is implemented by using KMDF instead of WDM. 3com 10/100 pci nic w/3xp (3cr990-tx-95) driver. This behavior differs from that of the legacy 1394 bus driver, in which certain I/O requests complete immediately.
A client driver must wait until I/O requests sent to the new 1394 bus driver are complete. You can provide an I/O completion routine that is called after the request is complete. Drivers sysgration input devices. The status of the completed I/O request is in the IRP.
Configuration ROM Retrieval
The new 1394 bus driver tries to use asynchronous block transactions at faster bus speeds to retrieve the contents of a node's configuration ROM. The legacy 1394 bus driver uses asynchronous quadlet reads at S100 speed—or 100 megabits per second (Mbps). The 1394ohci.sys bus driver also uses the values that are specified in generation and max_rom entries of the node's configuration ROM header to improve the retrieval of the remaining content of the configuration ROM. For more information about how the new 1394 bus driver retrieves the contents of a node's configuration ROM, see Retrieving the Contents of a IEEE 1394 Node's Configuration ROM.
IEEE-1394-1995 PHY Support
The 1394ohci.sys bus driver requires a physical layer (PHY) that supports IEEE-1394a or IEEE-1394b. It does not support a PHY that supports IEEE-1394-1995. This requirement is due to the 1394ohci.sys bus driver's exclusive use of short (arbitrated) bus resets.
Microsoft 1394 Driver Download For Windows Xp
NODE_DEVICE_EXTENSION Structure Usage
Microsoft Ieee 1394 Driver Download Windows 7
A client driver can reference the device extension in the 1394 bus driver associated with the physical device object (PDO) for the device that the client driver controls. This device extension is described by the NODE_DEVICE_EXTENSION structure. In 1394ohci.sys, this structure remains at the same location as in the legacy 1394 bus driver, but the nonstatic members of the structure might not be valid. When a client driver uses the new 1394 bus driver, they must make sure that the data accessed in NODE_DEVICE_EXTENSION is valid. The static members of NODE_DEVICE_EXTENSION that contain valid data are Tag, DeviceObject, and PortDeviceObject. All other members NODE_DEVICE_EXTENSION are nonstatic, which the client driver must not reference.
Gap Count Optimization
The default behavior of the 1394ohci.sys bus driver is to optimize the gap count when it finds only IEEE 1394a devices on the 1394 bus, excluding the local node. For example, if the system that is running 1394ohci.sys has a host controller that complies with IEEE 1394b but all devices on the bus comply with IEEE 1394a, then the new 1394 bus driver tries to optimize the gap count.
Gap count optimization occurs only if the 1394ohci.sys bus driver determines that the local node is the bus manager.
The 1394ohci.sys bus driver determines whether a device complies with IEEE-1394a by the speed setting in the node's self-id packet. If a node sets both of the bits in the speed (sp) field in the self-id packet, then 1394ohci.sys considers the node to comply with IEEE-1394b. If the speed field contains any other value, then 1394ohci.sys considers the node to comply with IEEE-1394a. The gap count value that is used is based on table E-1 in the IEEE-1394a specification, which provides the gap count as a function of hops. The 1394ohci.sys bus driver does not compute the gap count. You can change the default gap count behavior by using a registry value. For more information, see Modifying the Default Behavior of the IEEE 1394 Bus Driver.
Microsoft 1394 Driver Download For Windows
Device Driver Interface (DDI) Changes
In Windows 7, the 1394 DDIs were changed to support faster speeds as defined by the 1394b specification and improved to simplify the development of 1394 client drivers. For more information about the general DDI changes that the new 1394 bus driver supports, see Device Driver Interface (DDI) Changes in Windows 7.
Microsoft 1394 Driver Download For Windows 7
Related topics
Microsoft 1394 Driver Download For Windows 10
The IEEE 1394 Driver Stack
Retrieving the Contents of a IEEE 1394 Node's Configuration ROM